In recent developments within the cybersecurity landscape, researchers have identified a surge in email phishing campaigns delivering a new malware loader called Latrodectus.
This malware is emerging as a potential successor to the well-known IcedID malware, posing significant concerns for cybersecurity professionals and enthusiasts alike across the globe.
Lets deep dive into this in detail ✌️
Also Read : Google Patches Chrome Zero Day Vulnerability
Infection Chain and Delivery Method
Starting from early March 2024, phishing campaigns employing Latrodectus have been observed.
These campaigns use oversized JavaScript files to exploit Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) capabilities, invoking msiexec.exe to install a malicious MSI file hosted on a WEBDAV share 😑
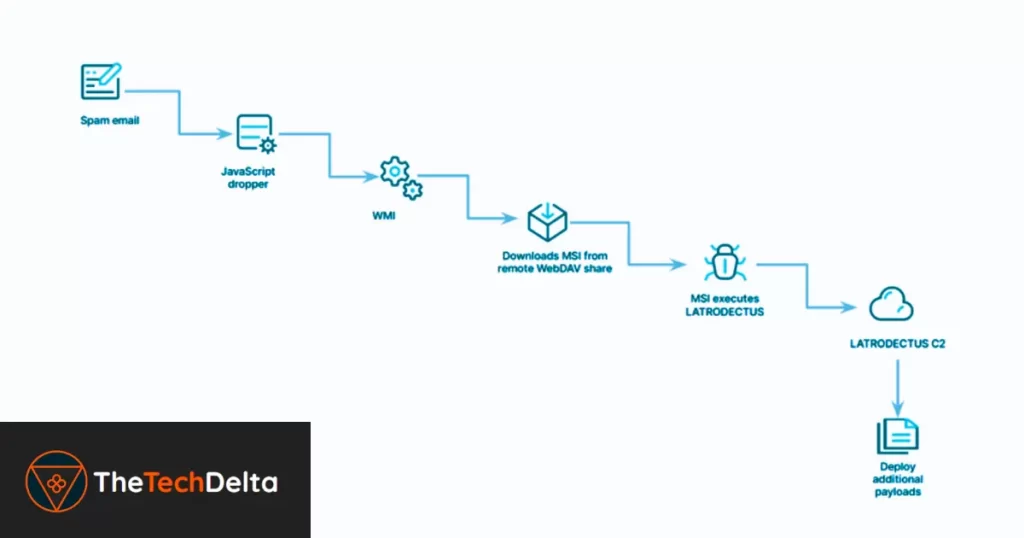
Researchers from Elastic Security Labs, Daniel Stepanic and Samir Bousseaden, have detailed this infection chain, check out the above image for a detailed understanding of the attack type and its various stages.
Capabilities and Functionality
Latrodectus is equipped with standard functionalities expected from malware loaders.
It can deploy various payloads like QakBot, DarkGate, and PikaBot, facilitating diverse post-exploitation activities.
Detailed analysis of Latrodectus artifacts reveals its focus on system enumeration, execution, and self-deletion techniques.
Evasion Techniques
To evade detection, Latrodectus masquerades as legitimate software libraries, employs source code obfuscation, and performs anti-analysis checks.
These measures ensure it can evade debugging or sandboxed environments, making it more challenging for cybersecurity defenses to detect and mitigate its presence 😓
Persistence and Command-and-Control
Latrodectus establishes persistence on Windows hosts via scheduled tasks and communicates with a command-and-control (C2) server over HTTPS.
This connection allows it to receive commands for collecting system information, updating, restarting, terminating itself, and executing shellcode, DLL, and executable files.
New Functionalities in Latrodectus Malware
Since its emergence, Latrodectus has incorporated two new commands by enumerating files in the desktop directory and retrieving the entire process ancestry from infected machines.
Notably, it supports a command (ID 18) to download and execute IcedID from the C2 server, suggesting a developmental connection between the two malware families.
Social Engineering and Phishing Campaigns
Forcepoint has analyzed phishing campaigns using invoice-themed email lures to deliver DarkGate malware.
These emails pose as QuickBooks invoices, prompting users to install Java via a malicious JAR file. The JAR file triggers a PowerShell script that downloads and executes DarkGate through an AutoIT script.
Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS)
An updated version of the phishing-as-a-service platform Tycoon has been observed, enhancing its detection evasion capabilities.
This platform targets Microsoft 365 and Gmail session cookies, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA) protections.
Proofpoint highlights significant obfuscation and dynamic code generation techniques in this new version, making it harder for security systems to identify and block.
Other Malware Campaigns
In March 2024, Google ads impersonating Calendly and Rufus propagated another malware loader known as D3F@ck Loader.
This loader, emerging in January 2024, drops Raccoon Stealer and DanaBot.
The case of D3F@ck Loader illustrates the evolving nature of malware-as-a-service (MaaS), using Extended Validation certificates to bypass security measures.
Emerging Stealer Malware
New stealer malware families like Fletchen Stealer, WaveStealer, zEus Stealer, and Ziraat Stealer have also been identified.
Additionally, the Remcos remote access trojan (RAT) has been using a PrivateLoader module to enhance its capabilities, employing VB scripts, registry alterations, and services to maintain persistence and evade detection.
Conclusion
The rise of Latrodectus and other advanced malware underscores the persistent and evolving threat landscape.
Cybersecurity professionals must stay vigilant and continuously update their defenses to combat these sophisticated threats.
Awareness and proactive measures are crucial in mitigating the risks posed by these emerging malware loaders and social engineering campaigns.
If you found these security learnings valuable, don’t miss out on more exclusive content. Follow us on Twitter and Instagram to stay informed about emerging threats and developments.
Check out the Cyber Safety Section and Subscribe our Newsletter, Join our community and gain access to the latest cybersecurity trends to bolster your defense against evolving threats & associated risks 🙂



