Several Android apps discovered on the Google Play Store have been identified as malicious, covertly transforming users’ devices into proxies for cybercriminal activities 😔
The alarming revelation stems from research conducted by HUMAN’s Satori Threat Intelligence team, uncovering a cluster of VPN applications equipped with a Golang library on these malicious android apps.
This covertly operating library discreetly transforms the user’s device into a proxy node without explicit consent.
Termed PROXYLIB by the research company, this discovery resulted in the removal of 29 implicated apps by Google, underscoring the severity of the threat.
Understanding Residential Proxies
Residential proxies constitute a network of proxy servers derived from genuine IP addresses provided by internet service providers (ISPs).
These proxies aid users in concealing their actual IP addresses by routing their internet traffic through intermediary servers. Despite the anonymity benefits they offer, residential proxies are susceptible to exploitation by threat actors.
These proxies not only obscure the origins of cyber attacks but also facilitate a wide array of malicious activities.
Exploiting Mobile Devices
Malware operators often exploit unsuspecting users by coercing them into installing deceptive applications, thereby roping their devices into a botnet. This botnet is then leveraged for profit by selling access to other nefarious actors.
The Android VPN apps identified by HUMAN serve to establish contact with remote servers, enrolling infected devices into the proxy network and executing requests from the network.
The Role of LumiApps SDK
A significant portion of these malicious apps, detected between May and October 2023, incorporate a software development kit (SDK) from LumiApps.
This SDK encompasses the proxyware functionality, enabling the malicious operations. Notably, LumiApps offers a service allowing users to upload APK files, including legitimate applications, and integrate the SDK without requiring a user account.
This enables the distribution of modified apps, referred to as mods, both within and outside the Google Play Store.
Expanding the Proxy Network via Malicious Android Apps
Evidence suggests that the threat actor behind PROXYLIB is capitalizing on the proxy network created by the infected devices, selling access through LumiApps and Asocks, a company specializing in residential proxies.
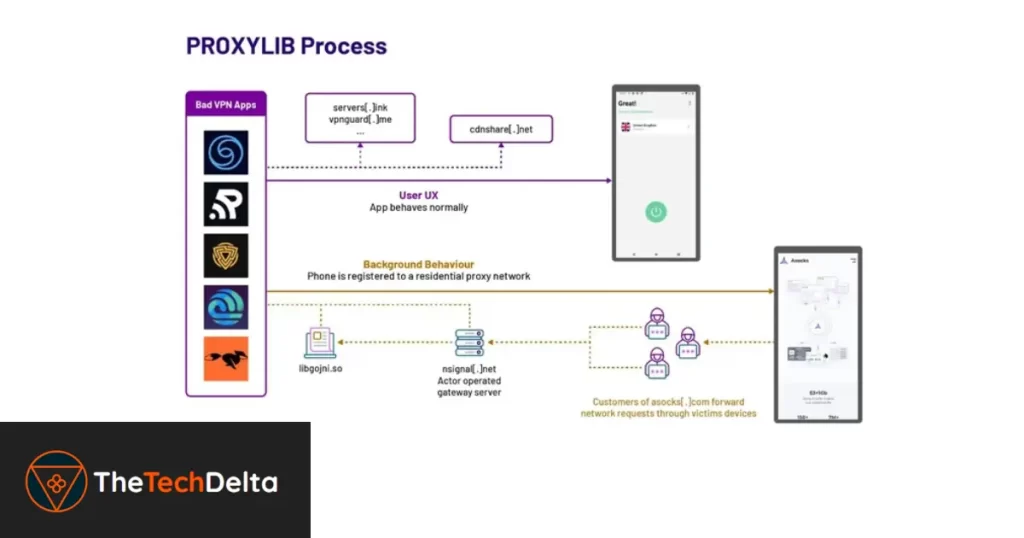
To proliferate the botnet further, LumiApps incentivizes developers with cash rewards based on the traffic routed through user devices hosting their apps.
This practice, along with the promotion of the SDK service on social media and black hat forums, exacerbates the proliferation of malicious proxies.
The Transparency Issue
The research conducted by Orange Cyberdefense and Sekoia brings to light a significant issue surrounding the transparency of proxyware installation.
This lack of clarity is particularly concerning as proxyware is often embedded within various products or services. Users, unaware of the presence of proxyware, might unknowingly consent to its installation while accepting the terms of use of the primary application.
This opacity in the installation process not only compromises users’ privacy but also contributes to the expansion of botnets, as their internet connections are unwittingly utilized for malicious activities.
Therefore, enhancing transparency in the installation of proxyware is imperative to safeguarding users against inadvertent involvement in cybercriminal schemes and mitigating the proliferation of botnets.
The Rise of Criminal Proxy Services
The disclosure made by Lumen Black Lotus Labs regarding the compromise of end-of-life (EoL) small home/small office (SOHO) routers and IoT devices by TheMoon botnet is particularly alarming.
This revelation sheds light on the vulnerabilities inherent in such devices, especially when they reach the end of their lifecycle. The exploitation of these devices by TheMoon botnet to power a criminal proxy service named Faceless emphasizes the pervasive nature of malicious proxy networks.
This highlights the urgent need for improved cybersecurity measures to address vulnerabilities in IoT devices and routers, mitigating the risk of exploitation by botnets and criminal actors.
Increased awareness and proactive security measures are essential to safeguarding against such threats and protecting the integrity of networks and devices.
Conclusion
The infiltration of Android devices by malicious apps, converting them into proxies for cybercriminal activities, underscores the pressing need for heightened vigilance and stringent security measures.
The exploitation of residential proxies poses significant risks, necessitating collaborative efforts from cybersecurity experts, app developers, and platform providers to mitigate such threats effectively.
Enhanced transparency regarding the installation of proxyware and proactive measures to detect and remove malicious apps are extremely important in safeguarding users against the proliferation of criminal proxy networks.
If you found these security learnings valuable, don’t miss out on more exclusive content. Follow us on Twitter and Instagram to stay informed about emerging threats and developments.
Check out the Cyber Safety Section and Subscribe our Newsletter, Join our community and gain access to the latest cybersecurity trends to bolster your defense against evolving threats & associated risks🙂



